Unique selling points
- Early Detection of Issues: Early detection of infiltration allows for proactive intervention, preventing potential system overflows, backups, and associated environmental hazards.
- Cost-Effective Solution: By accurately pinpointing infiltration points, the technology enables targeted repairs and maintenance, minimizing the need for costly and disruptive system-wide upgrades.
In recent years, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has revolutionized the field of urban infrastructure management, particularly in the context of wastewater systems. Among the myriad applications of IoT in this domain, the detection and monitoring of infiltration in sewer networks have emerged as crucial areas of focus. Infiltration, characterized by the ingress of groundwater or rainwater into sewer pipes through defects or improper connections, poses significant challenges to the efficient operation of sewerage systems, leading to increased treatment costs, overwhelmed capacity, and environmental concerns. Traditional methods of infiltration detection often involve labor-intensivelabour-intensive and time-consuming processes, making them inefficient for comprehensive network monitoring. However, the advent of IoT sensors technology offers a promising solution by enabling real-time, remote monitoring of sewer networks, thereby enhancing detection capabilities and facilitating proactive management strategies.
Description of the technology
IoT sensors technology for infiltration detection in the sewer network leverages a network of advanced sensors strategically deployed at key points within the sewer infrastructure. These sensors continuously monitor and record the flow of wastewater into and out of the designated examination area at short, high-resolution intervals. By precisely measuring the flow rates during both dry and wet weather conditions, the technology enables the identification and quantification of excess water entering the sewer network. Through sophisticated data analysis algorithms, the system discerns fluctuations in flow patterns, distinguishing between normal wastewater flow and infiltration-induced surges. This granular understanding allows for the precise determination of the volume and timing of infiltration events, facilitating targeted interventions to mitigate infiltration and optimize sewer system performance.
Flow scheme of the technology
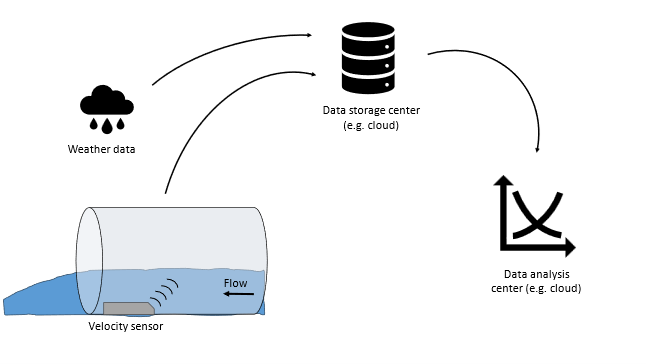
Synergetic effects and motivation for the implementation of the technology
Improved Leak Detection: By continuously monitoring wastewater flow rates and patterns in sewer networks, IoT sensors technology enables early detection of leaks, cracks, and infiltration points in the system.
Cost Savings: Detecting and mitigating infiltration can lead to significant cost savings for utilities by reducing the volume of excess water treated at wastewater treatment plants. By accurately quantifying infiltration rates and implementing targeted interventions to address infiltration sources, utilities can optimize wastewater treatment processes, minimize energy consumption, and reduce operational expenses associated with treating and conveying excess water.
Environmental Protection: Minimizing infiltration in sewer networks helps prevent the discharge of untreated or partially treated wastewater into the environment, safeguarding water quality and ecosystem health.
Regulatory Compliance: Many regulatory agencies require utilities to monitor and manage infiltration levels in sewer networks to comply with environmental regulations and discharge permit requirements. IoT sensors technology provides utilities with the tools and data needed to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards, track performance metrics, and report on infiltration reduction efforts, ensuring accountability and transparency in environmental stewardship.
Technology requirements and operating conditions
Data Transmission: The sensors must be equipped with reliable data transmission capabilities to facilitate real-time data transfer from the field to a centralized monitoring system. This may involve wireless communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, cellular, or LoRaWAN to ensure seamless connectivity.
Power Supply: Continuous power supply is critical for uninterrupted sensor operation. Depending on the deployment location, sensors may be powered by mains electricity, battery packs, or solar panels to ensure reliable power availability.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the sensors are essential to ensure accurate measurements and optimal performance over time. Scheduled maintenance tasks may include sensor recalibration, battery replacement, and cleaning to prevent sensor fouling and degradation.
Links to related topics and similar reference projects
- Assessing infiltration and exfiltration on the performance of urban sewer systems (APUSS) (https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/EVK1-CT-2000-00072)
- A Smart Technology Trained for Preventing Leakages from Sewer Systems (https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/697140/reporting)

